Stem Cells and Diabetes
Diabetes type 1
Hyperglycemia is a common contributor to a number of complications like
• Heart and vascular diseases Stem Cells and Diabetes
• Eye and kidney complaints
• Poor vascularisation
• Damage to nerve cells (neuropathy)
• Diabetic feet
• High susceptibility for infections
• Erectile penile dysfunction
Diabetes type 2
What are stem cells and why are they important?
Stem cells have two important characteristics that distinguish them from other types of cells.
What are adult stem cells?
For more information visit us at,
http://www.mvdiabetes.com
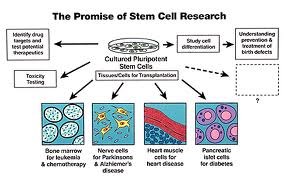
For decades, diabetes researchers have been searching for ways to replace the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas that are destroyed by a patient’s own immune system. Research on stem cells is advancing knowledge about how an organism develops from a single cell and how healthy cells replace damaged cells in adult organisms.
Diabetes type 1
The autoimmune reaction of the body to the pancreatic beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans and the resulting destruction of these beta cells, cause an immediate insulin deficiency, resulting in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes mellitus type 1 is a degenerative disease, which is traditionally treated using insulin injections. These injections
replace the missing hormone, but the complications can be farreaching.
replace the missing hormone, but the complications can be farreaching.
Hyperglycemia is a common contributor to a number of complications like
• Heart and vascular diseases Stem Cells and Diabetes
• Eye and kidney complaints
• Poor vascularisation
• Damage to nerve cells (neuropathy)
• Diabetic feet
• High susceptibility for infections
• Erectile penile dysfunction
Diabetes type 2
Type 2 diabetes used to be known as maturity onset, or noninsulin dependent diabetes. Although type 2 diabetes typically affects individuals over the age of 40, today it occurs at an increasingly younger age, especially in people who have a family history of diabetes. Diabetes mellitus type 2 is the most common form, affecting 85 - 90% of all people with diabetes. Experts estimate that nearly one-third of people who have type 2 diabetes don’t even know it.
What are stem cells and why are they important?
Stem cells have two important characteristics that distinguish them from other types of cells.
• They are unspecialised cells that renew themselves for long periods through cell division.
• Under certain physiologic or experimental conditions, they can be induced to become cells with special functions such as the beating cells of the heart muscle or the insulinproducing cells of the pancreas.
• Under certain physiologic or experimental conditions, they can be induced to become cells with special functions such as the beating cells of the heart muscle or the insulinproducing cells of the pancreas.
• Milk, Yogurt and Cheese: 2-4 servings a day 1 serving = 1 cup milk or yogurt, 1 oz natural cheese, 2 oz processed cheese.
• Meat, Poultry, Fish, Dry Beans, Eggs and Nuts: 2-3 servings a day 1 serving = 3 oz cooked lean meat, poultry or fish; 1 egg; 1/2 cup cooked beans; 2 tablespoons peanut butter, nuts or seeds.Couple the Food Guide Pyramid with practical food portion measurements and you’ve got an easy and pretty accurate way to gain control over the amount of food you eat.
• Meat, Poultry, Fish, Dry Beans, Eggs and Nuts: 2-3 servings a day 1 serving = 3 oz cooked lean meat, poultry or fish; 1 egg; 1/2 cup cooked beans; 2 tablespoons peanut butter, nuts or seeds.Couple the Food Guide Pyramid with practical food portion measurements and you’ve got an easy and pretty accurate way to gain control over the amount of food you eat.
What are adult stem cells?
Adult (Somatic) stem cells are unspecialized cells that are found in different parts of the body and, depending on the source tissue, have different properties.
• Adult stem cells are capable of self-renewal and give rise to daughter cells that are specialized to form the cell types found in the original body part.
• Adult stem cells multi-potent, meaning that they appear to be limited in the cell types that they can produce based on current evidence. However, recent scientific
• Adult stem cells are capable of self-renewal and give rise to daughter cells that are specialized to form the cell types found in the original body part.
• Adult stem cells multi-potent, meaning that they appear to be limited in the cell types that they can produce based on current evidence. However, recent scientific
For more information visit us at,
http://www.mvdiabetes.com